
Only one mode propagates if V, in this case it is called a single mode guide.įind the maximum waveguide core thickness d for a device with n 1 =1.48 and n 2 = 1.46 and a wavelength of 1 μ m to achieve single mode propagation. The frequency of the transmitted wave also dictates the size of a waveguide: each waveguide has a cutoff wavelength determined by its size and will not conduct waves of greater wavelength an optical fiber that guides light will not transmit microwaves which have a much larger wavelength. The number of guided modes in a step-index guide (N) is given by If you decrease the thickness you decrease the number of modes that can propagate. The numerical simulations reveal the high sensitivity of the guided mode intensity near the cut-off wavelength for any refractive index change along the waveguide. Thus the mode shift depends on the relative index of refraction of the materials and the thickness of the waveguide. Near cut-off and far from cut-off modes are investigated, and their characteristics and suitability for sensing are compared. V is the normalized film thickness, normalized frequency, or V parameter We write the phase change resulting from reflection simply as δ(θ)įor perpendicular radiation φ (θ) is 2 ψ, for parallel radiation φ(θ) = 2 δ.
Can u provide the literature or link from where I can get some useful information about this. the characteristic impedance of the guide becomes infinite. This example is for TE 1,0 (the mode with. the phase velocity of the signal becomes infinite. The lower cutoff frequency (or wavelength) for a particular mode in rectangular waveguide is determined by the following equations (note that the length, x, has no bearing on the cutoff frequency): Rectangular Waveguide TE m,n Mode. each one centred at a different wavelength. the group velocity of the signal becomes zero. Analysis of lossy mode cut-off conditions in planar waveguides with semiconductor guiding layer.
CUT OFF WAVELENGTH OF A PLANAR WAVEGUIDE FREE
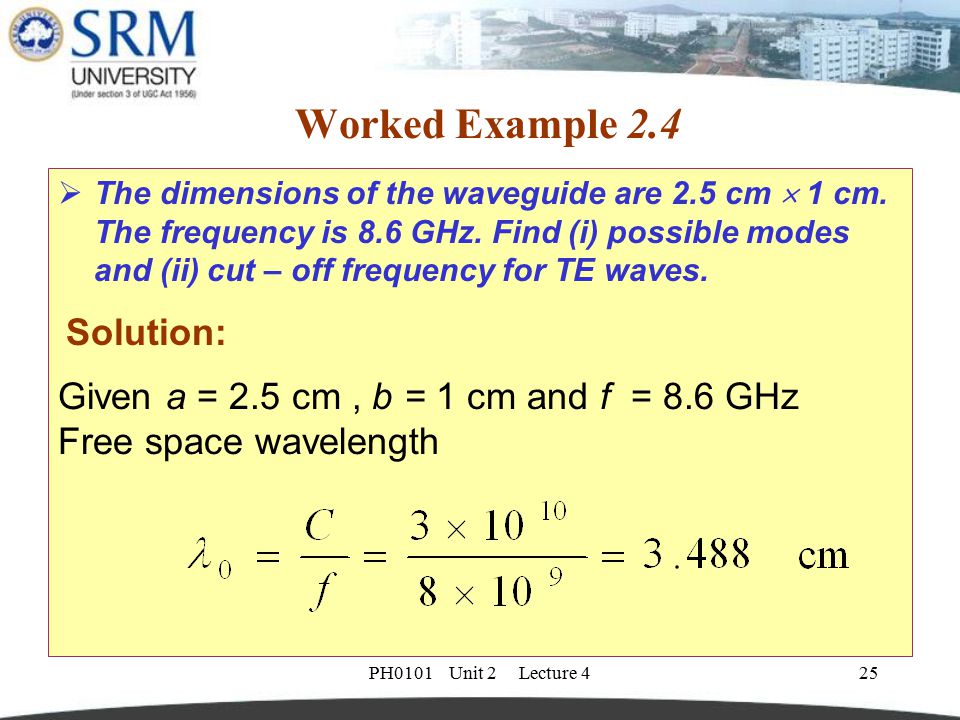
What will be the radius of circular waveguide if it is to operated at 8.2 GHz. When the free space wavelength of a signal equals the cut-off wavelength of the guide. the phase change due to reflection at B and C circular waveguide cutoff frequency Hi, Can somebody tell me the specific formula to calculate the cutoff frequency of circular waveguide. It also requires very specific angles θ above the critical angle.Ĭonsider the phase difference between A and C Otherwise there would be destructive interference between out-of-phase waves and the light will not propagate. Therefore the phase at C and A must be the same or differ by a multiple of 2π. The wavefront FC intersects tow the upwardly traveling portions of the same ray at points A and C. MHz wave to propagate inside the waveguide, the cutoff frequency must be lower then the mode of propagation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
